The additional lead-in path is the traverse path required by some machines during ignition for breaking through the material.
The archive browser is used to manage the archive and its contents.
An assembly loop is a loop than can only be used on 3D assemblies.
A beam tool is a tool that produces a jet for material processing. This includes, for example: Laser, plasma, torch, water, sand.
Breakthrough is the initial penetration of the material by the beam of the beam tool (laser, water, torch ...).
The bridge lug is the part of a cutting bridge that represents the initially remaining unmachined contour.
During manual moving of parts in a nesting, the collision check ensures that contours do not overlap and that the set distances are maintained.
Common Cut refers to a process in which two workpieces are separated by a common separating cut. In the process, material waste is reduced to almost zero for suitable parts and cutting and clearing time is significantly reduced.
Contour damage is damage to a contour due to machining.
The contour overcut is a corner parameter that specifies how far a loop or triangle may project beyond the contour of the part during corner machining.
A contour type is the type of machining by the production machine that applies to an NC element.
Corners elements are the geometry elements that together form a corner.
Corner types differentiate the shape of a corner or the different types of machining by the tool.
A cutout is the setting of a cut that serves as a breakthrough into which a beam tool can later plunge with an inclined beam when using a beam tool.
A cutting bridge is an additional geometry element that connects two parts. This allows for continuous machining without stopping and resuming cutting.
Dead points are the end positions of the stroke movement of a punching tool. Accordingly, there is a lower and an upper dead point.
Dead points are the end positions of the stroke movement of a punching tool. Accordingly, there is a lower and an upper dead point.
The dead zone of a tool is defined as the area where the use of the tool will damage other, already performed, machining operations.
The dead zone of a tool is defined as the area where the use of the tool will damage other, already performed, machining operations.
Difference parts are parts that deviate from the target quantity of the order by being too numerous or too lacking in the current nesting.
Disposal is a system used on laser and punching machines to eject separated parts from the work area.
The equidistant is a straight line or curve parallel to the contour of a workpiece.
Filler parts are parts that are subsequently nested on free spaces of an existing nesting to increase the utilisation of the sheet.
A free space is the area of a sheet that is not occupied with parts.
A free space is the area of a sheet that is not occupied with parts.
A geometry nesting is a nesting method by which the parts are nested according to their actual geometry. Suitable function for parts with irregular shape.
The gross area is the surface area of a complete sheet.
A hull rectangle is the smallest possible rectangle that can be formed parallel to the coordinate axes around a part in the current position.
The ignition hole is the breakthrough created in the material by the tool beam at the ignition point.
An ignition point is the position at which the tool beam pierces through the material from above.
When gradually increasing or decreasing a size or variables, an increment or decrement is the specified amount of change. Latin: incrementare/decrementare
An inner contour represents the edge of a cut-out of a part.
An inner contour represents the edge of a cut-out of a part.
An inside corner is a corner that projects into a contour of the part. From the tool's point of view, the corner angle is less than 180°.
An inside corner is a corner that projects into a contour of the part. From the tool's point of view, the corner angle is less than 180°.
An interior surface is a surface within the outer contour of a part.
An interior surface is a surface within the outer contour of a part.
A job is the nesting of one or more production orders.
Job data are the data that are transmitted to the production machine for the machining.
The lead-in is the first machining step that machines the contour of a part.
To ensure that the laser pierce (piercing hole) does not lie directly on the contour, an additional step, the lead-in path, is necessary. Thus, the workpiece remains "clean".
The lead-in point is the point at which the lead-in path meets the contour of the part.
A lead-out is any departure from the contour during a machining step.
The lead-out path is an additional machining step. Here, the contour is moved away from after the cut has been made so as not to leave any irregularities on exit.
A loop is a sequence of functions determined by the user and that is automatically executed when called up.
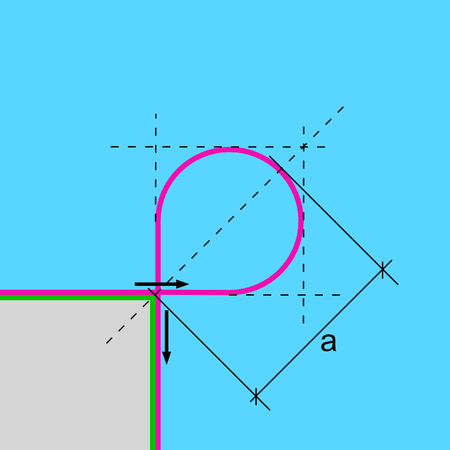
A loop corner is a type of corner where the tool moves between the corner elements of a loop. This allows the contour to be left straight or cut.

A loop corner is a type of corner where the tool moves between the corner elements of a loop. This allows the contour to be left straight or cut.
A macro is a sequence of NC blocks that is determined by the user and that is assigned to a geometry. The sequence is automatically inserted when the assigned geometry is present in a part.
The material pool is a management system for sheets that is available for nestings.
A mini-nesting is a nesting that only contains one same part that is produced several times.
A multiple tool is a punching tool that punches several holes with one punching stroke.
A multiple tool is a punching tool that punches several holes with one punching stroke.
The nesting base is the basic file in which the parts and sheets of the nesting are entered.
The nesting base is the basic file in which the parts and sheets of the nesting are entered.
A nesting limit is a virtual line determined by the user and that serves in a nesting as a border that is not overcut.
The net area is the actually utilised area of a sheet.
The order pool is the management system for production orders. Here, new orders are saved and existing orders are retrieved for production.
The outer contour represents the outer edge of a part.
The outer contour represents the outer edge of a part.
An exterior surface is a surface outside the outer contour of a part.
An exterior surface is a surface outside the outer contour of a part.
An outer corner is a corner that protrudes from a contour of the part. From the tool's point of view, the corner angle is greater than 180°.
An outer corner is a corner that protrudes from a contour of the part. From the tool's point of view, the corner angle is greater than 180°.
A part loop is a loop that can only be used on parts.
Path compensation ensures that the tool path is offset by the radius of the tool, thus avoiding contour errors.
The path offset is the value by which the tool path is offset for path correction. It is equivalent to the radius of the tool.
Piercing is the initial penetration of the material with the beam of the beam tool (laser, water, torch, etc.).
Piercing types are the different methods by which a beam tool can pierce.
In pixel nesting, all parts to be nested are individually and successively well positioned on the sheet using the snap grid.
In place nesting, if possible, the entire quantity of a part is positioned freely on the sheet in the favourable parquet arrangement.
A plat loop is a loop that can only be used on sheets.
In elementary geometry, a polygon is a flat geometrical shape that is formed or limited by a closed traverse line.
A polyline is an open polygon.
A post-processor is a computer program that converts the results of a CAM program into a CNC format.
In power nesting, if possible, the entire quantity of a part is positioned on the sheet in a favourable arrangement using the snap grid.
In PN4000, a PP run is the creation of a CNC program by the post-processor.
In a combination machine, a pre-punch hole is a punched hole that saves a tool jet from breaking through the material.
The pre-rotation angle is the angle difference that defines another angular position for a part for a nesting, based on the orientation upon creation of the part.
A rectangle nesting is a nesting method in which the parts are nested based on their hull rectangle.
The reference geometry is the geometry assigned to a macro as reference.
A remnant sheet is the part that remains from an incompletely used sheet after machining.
When reorganising, existing geometries are read again.
Repositioning is the relative re-positioning of the workspace with respect to the workpiece in a machine, in order to gradually fully machine oversized workpieces.
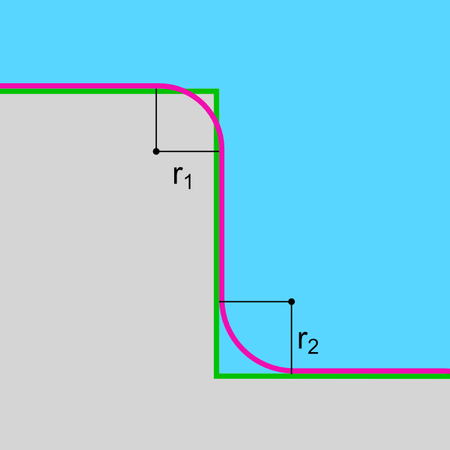
A rounded corner is a type of corner where a corner is rounded off with a certain radius for machining.

A rounded corner is a type of corner where a corner is rounded off with a certain radius for machining.
The rotation increment indicates the number of increments for a complete rotation of a part. Step size is the amount by which a variable increases incrementally.
Scrap are parts that are faulty. These are not used as parts.
Dropdown menu from which elements can be selected in the program workspace.
Selection modes are the different methods by which elements in the workspace can be selected.
A separation line is a virtual line determined by the user and that serves in a nesting as a border where the separation cut is made after machining to cut off the rest of the sheet.
A sheet is a product of a flat rectangular shape that is suitable for processing on punching or cutting machines.
The snap grid limits the definition of the individual elements on a grid with definable distances in order to create rectangular polygons.
A standard nesting is a nesting that is repeatedly used as a template, because the parts contained therein must be repeatedly produced.
A starting trough is an additional geometry element that prevents residues of the material from protruding beyond the contour at the lead-in point. The contour is consequently offset in the negative area in a trough-like manner at the lead-in point.
The tool beam is the beam of a beam tool.
A torch is a beam tool on flame cutting machines that uses an ignited gas or plasma jet to machine the material.
The torch arrangement indicates the direction in which the torches are arranged for multi-torch systems.
A torch copy is the geometry that is created on a multi-torch system by implementing the NC blocks for multiple torches.
A torch stage is the resetting of the torch gantry to machine a new part sequence of a nesting in multi-torch systems.
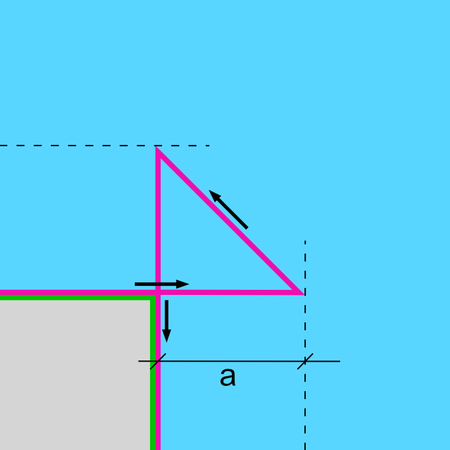
A triangle corner is the type of corner where the tool moves in a triangle between the corner elements. This allows the contour to be left straight or cut.
Vapourising is the partial removal of a protective film on the material to be cut. Since the film would melt during laser cutting, it is cooled by a gas mixture, but this causes it to fluff up and the laser head can get stuck during cutting. To avoid this, before the contour cut the laser makes a circle and allows the film to evaporate at this point. Thus, it can pierce and cut without the film fluffing up.
A variant is a variation of a part, whereby details are changed but the intended use remains the same.
A Z lug is a lug whose height is defined in the Z direction and that does not correspond to the full material thickness.
